If you’re an avid gamer or use your computer for graphics-intensive tasks, a well-performing GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is crucial for a smooth experience. However, you might find yourself wondering, “Why is my GPU not performing as expected?” In this article, we’ll delve into the common issues that can hamper GPU performance and provide practical fixes to get your GPU running smoothly.
7 Reasons Why Your GPU Is Underperforming
- Outdated Graphics Drivers
- Overheating
- Dust and Dirt Buildup
- Insufficient Power Supply
- Software Conflicts
- Hardware Issues
- Background Processes and Multitasking
1. Outdated Graphics Drivers
Outdated graphics drivers can have a significant impact on GPU performance. Firstly, outdated drivers often lack optimizations for newer games and applications, leading to reduced performance and potential compatibility issues. This lack of optimization can result in sluggish gameplay and lower frame rates, making it challenging to enjoy the latest gaming experiences.
Moreover, security concerns arise with outdated drivers. These drivers may not have essential security updates and patches, leaving your system vulnerable to potential threats. Ensuring the security of your GPU drivers is crucial in maintaining a safe computing environment.
On the other hand, keeping your graphics drivers up-to-date can provide several benefits. When you update your drivers, you may experience performance boosts as newer versions often include optimizations and bug fixes that enhance overall system stability and responsiveness. These updates can translate into smoother gaming experiences and faster rendering times.
2. Overheating
Overheating can have a profound effect on GPU performance, leading to various consequences. Firstly, excessive heat can cause the GPU to throttle. When the temperature rises beyond safe limits, the graphics card may automatically reduce its clock speed and performance to prevent damage. This results in a noticeable drop in frame rates and overall graphical performance.
Furthermore, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to hardware damage. Overheating may cause components such as capacitors and solder joints to deteriorate, potentially resulting in permanent hardware failure. This can be a costly consequence, as it necessitates repairs or even a replacement of the GPU, leading to downtime and expenses.
Transitioning from the hardware perspective to the software side, overheating can affect GPU performance by causing thermal throttling. In such cases, the GPU’s frequency states may transition to lower performance modes to manage heat, resulting in suboptimal performance for demanding tasks.
3. Dust and Dirt Buildup
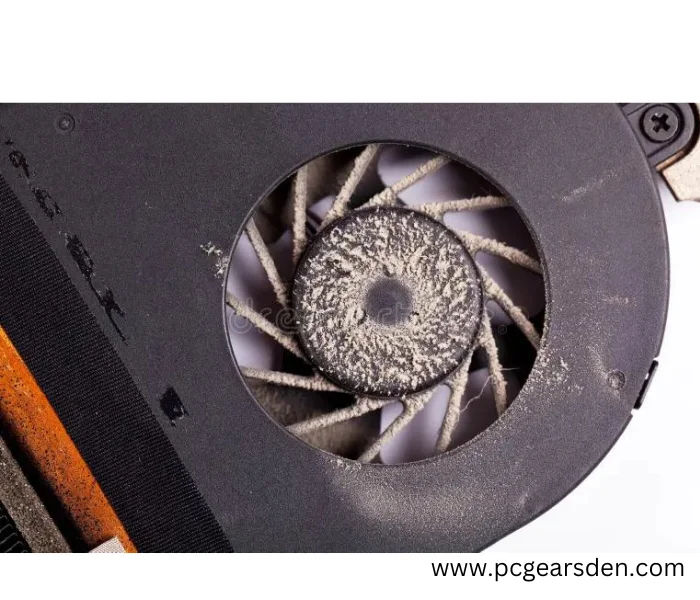

The accumulation of dust and dirt inside your computer can have a notable impact on GPU performance. Dust and dirt act as insulators. When they settle on the GPU and its components, they form a layer that traps heat. This insulating effect hinders the GPU’s ability to dissipate heat efficiently, causing it to operate at higher temperatures. Elevated temperatures can lead to thermal throttling, where the GPU reduces its clock speed to prevent overheating. Consequently, this results in degraded performance as the GPU operates below its optimal speed.
Moreover, dust and dirt can clog the cooling system of the GPU, including fans and heatsinks. This impedes the flow of air and disrupts the cooling mechanism’s effectiveness. As a result, the GPU can reach even higher temperatures, exacerbating thermal throttling and further diminishing performance.
Additionally, the accumulation of contaminants can lead to component corrosion over time. Dust and dirt can attract moisture, creating a corrosive environment that may harm sensitive GPU components. This corrosion can cause permanent damage and result in the need for costly repairs or replacement of the graphics card.
4. Insufficient Power Supply
The impact of an insufficient power supply on GPU performance is substantial, insufficient power delivery to the GPU can result in underclocking or throttling. When the GPU doesn’t receive the required power, it reduces its clock speed to stay within the available power limits. This is a protective measure to prevent overloading the power supply but leads to a significant drop in performance.
Furthermore, inadequate power can cause system instability. When the GPU draws more power than the power supply can provide, it can lead to system crashes and sudden shutdowns, interrupting your computing tasks and potentially causing data loss.
Moreover, insufficient power can affect the GPU’s ability to perform tasks efficiently. In cases where the GPU doesn’t get the necessary power, it might struggle to render complex graphics, resulting in laggy or stuttering gameplay, which is especially noticeable in graphically demanding applications.
5. Software Conflicts
Software conflicts can significantly impact GPU performance in various ways as they can cause stuttering and frame drops in graphics-intensive applications. When conflicting software components compete for GPU resources, it can result in inconsistent frame rendering. This inconsistency leads to a jarring user experience, especially in video games and multimedia applications.
Furthermore, these conflicts can result in increased CPU utilization. When software components do not coordinate efficiently with the GPU, the CPU may need to compensate for the lack of synchronization. This additional CPU load takes away processing power that could be dedicated to GPU tasks, leading to reduced overall system performance.
Moreover, software conflicts can also lead to system crashes and instability. In cases where conflicting software components try to access the GPU simultaneously or misuse its resources, it can result in driver crashes or even system-wide instability, requiring system reboots and causing data loss.
Additionally, conflicts can affect the efficiency of GPU memory usage. When multiple software components allocate and release GPU memory without proper coordination, it can lead to memory leaks and inefficient memory management, reducing the GPU’s ability to handle large datasets efficiently.
6. Hardware Issues
Aging or defective hardware components on the GPU itself, such as a malfunctioning fan or damaged connectors, can directly impact performance.
Overheating due to inadequate cooling can lead to thermal throttling. When a GPU gets too hot, it may automatically reduce its clock speed to prevent damage. This results in lower performance as the GPU operates below its optimal speed.
Furthermore, hardware issues such as a faulty power supply can cause insufficient power delivery to the GPU. In such cases, the GPU may not receive the required voltage and current, leading to instabilities and crashes during demanding tasks.
Moreover, dust and dirt within the GPU and its components can accumulate over time, restricting airflow and causing heat retention. This can exacerbate overheating issues, leading to thermal throttling and reduced performance.
7. Background Processes and Multitasking
Background processes and multitasking can significantly impact GPU performance, leading to both challenges and opportunities in modern computing.
When multiple applications run concurrently, the operating system allocates GPU resources based on priorities. Transitioning between these tasks involves task switching, where the CPU pauses one task to execute another. While this ensures fair resource sharing, it can lead to performance fluctuations as the GPU reallocates its processing power.
GPUs used for parallel processing, such as in scientific applications or machine learning, concurrent tasks can experience scalability slowdown. This occurs when the GPU’s computational capacity is divided among multiple tasks, causing each task to perform suboptimally. Scalability slowdown can limit the overall performance gain from GPU parallelism.
Background processes, like system updates or software downloads, may compete for GPU resources, causing temporary performance drops in foreground applications. GPUs must dynamically allocate resources to meet the demands of both foreground and background tasks, leading to fluctuations in performance.
Memory Management in multitasking and background processes can also affect GPU memory usage. Context switching between applications requires memory allocation and deallocation, potentially leading to memory fragmentation and suboptimal memory utilization, impacting overall performance.
Solutions for Improved GPU Performance
Now that we’ve identified the common issues affecting GPU performance, let’s explore the solutions that can help you get the most out of your graphics card.

Clean your computer
One of the first things you can do to boost the performance of your GPU is to clean the air that your computer is “breathing.”
Dust can cause a variety of issues with your computer, including overheating and decreased performance.
Here’s how to thoroughly clean your computer.
- Power off your computer. Make sure no apps are active on your computer before proceeding.
- Remove any unnecessary wires. This will include USB and audio cords, among other things.
- Remove your power supply from the case and store it somewhere safe.
- If you don’t want to take the trouble to remove it, simply unplug it from its outlet.
- Blow out any dust that has gathered inside your system with compressed air.
This solution provides excellent airflow at a reasonable cost and enough power to affect how quickly your GPU performs instructions.
Upgrade the cooling system
A good cooling system operates more quickly and efficiently. In order to get rid of extra heat, you may need to replace your old one or effectively control fan speed our your computer to work more efficiently.
This can be done by using different software and other solutions or adding more fans. You can read about “How To Effectively control GPU Fan Speed” to help you sort out any fan speed configuration issues in another one of my articles.
But, before you do so, make sure your graphics card design is compatible with the cooling system you intend to install.
Additionally, make sure that your graphics card fans accelerate as the temperature rises. If not, you should consider installing something like MSI Afterburner and adjusting the fan speed profile. Upgrading the cooling system can ultimately help solve your GPU not performing problem.
Install and Update your Drivers
If your GPU is significantly outdated or struggles to keep up with modern demands, it might be time for an upgrade. Upgrading your GPU can result in a substantial performance boost for your system.
When you play a game, you want the most recent manufacturer updates installed on your computer.
An updated driver keeps the system and associated hardware compatible with newer and more complex video games.
Conclusion
In conclusion, your GPU’s performance is essential for a smooth computing and gaming experience. By addressing common issues such as outdated drivers, overheating, and software conflicts, and by implementing solutions like regular maintenance, hardware upgrades, and performance